Tech Support for Pollution Control
Tech Support for Pollution Control
Air quality has been constantly degraded due to pollution arising out of the industrial sector. The reduction in industrial emissions in order to minimize its environmental & health effects is a major concern in developing economy like India. There are a number of Air Pollution Control and Monitoring Technologies available in the market, but it is difficult to make decisions in choosing the most suitable technologies, especially due to absence of comparative assessments, experts’ opinions and lack of knowledge on efficient latest technologies. The System Design plays the most important role in the performance of the Air Pollution Control Devices.
PSCST is proactively providing technology support to the MSMEs on pollution control on chargeable basis w.r.t. designing and adequacy check of Air Pollution Control system. PSCST has satisfied clientele of more than 7000 MSMEs during the last 27 years which include foundry units, rice shellers , brick kilns, re-rolling mills, induction furnace, etc.
The Council provides technical consultancy for air pollution control to industry. The gamut of work includes visits to industry, in-plant diagnostic study, preparation of feasibility report containing technical specifications and drawings of pollution control device (APCD), standard operational practices (SOPs), training to the APCD operator and finally issuing completion and adequacy certificate for APCD.
The Council has demonstrated energy efficiency and pollution control technologies in various industrial clusters that has contributed in terms of cleaner environment besides additional savings to the industry. These technologies have a payback period of one to two years only. Following are some of the clusters wherein Council has made significant contribution in the last three decades:-
Tech-interventions for air pollution control in Textile & Dyeing Industrial Sector

Ludhiana, occupies a predominant position in textile map of India wherein around 300 small & medium textile dyeing units are in operation. The Ludhiana dyeing cluster carries out dyeing and processing of grey fabric, with many units producing finished fabric used by garment units in Punjab and other regions of Northern India. These industrial units have installed boilers of capacity ranging from 2 10 Ton/Hour for steam generation. Biomass and pet coke are commonly used fuel in their furnaces for steam generation. Air Pollution Control Device in the form of cyclone/ scrubber has been installed to contain emissions from these boilers. The Industrial cluster of Ludhiana has been identified as one of the critically polluted clusters by the Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change, Govt. of India.
A source apportionment study for controlling Air Pollution in Ludhiana city carried out by PSCST has revealed that the textile dyeing cluster contributes 25% of the total PM10 emissions from the industrial sector in Ludhiana. Moreover, black smoke being emitted intermittently from such dyeing units is deteriorating the ambient air quality of the region.
It has been felt necessary to demonstrate a scientifically designed Air Pollution Control System which would be able to capture most of the emissions being generated in the furnace section of the dyeing unit. Moreover, better fuel firing practices need to be introduced to cut down the black smoke from furnace stack being emanated from this industrial sector.
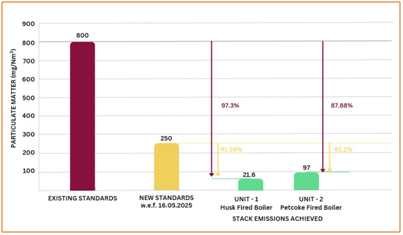
PSCST carried out detailed baseline studies in about 15 dyeing units using varied quality of fuel. Thereafter, an Air Pollution Control technology has been designed and successfully demonstrated in two units using paddy husk & pet coke as fuel with support of Mission Tandarust Punjab of Directorate of Environment and Climate Change, Govt. of Punjab. In rice husk based textile dyeing unit, Pulse Jet Bag Filtration technology has been demonstrated. Whereas, two stage scrubbing technology i.e. impingement type scrubber followed by packed bed scrubber has been demonstrated in pet coke based boiler. The demonstrated systems are working at an efficiency of more than 90% and are able to address the problem of black smoke being emitted from stacks besides bringing down the particulate matter to less than 100 mg/Nm³. Moreover, with the use of better scrubbing technology along with good operating practices, the SO2 emissions have reduced and are well below the prescribed emission standards. The demonstrated technology is also able to achieve the revised stringent emission standards notified by Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC), Gol in 2023. It has been envisaged that the pollution load would be reduced to the tune of 6500 tons/annum with the adoption of this tech-intervention by the dyeing cluster of Ludhiana which would in turn lead to improvement in ambient air quality of Ludhiana one of the non-attainment cities of the State.
Tech-interventions to control air pollution in Plywood Manufacturing Industrial sector

Plywood is an important construction material widely used in building projects. It is manufactured from thin layers of wood veneer, which are glued together to achieve the desired thickness. In the State of Punjab, there are approximately 150 plywood manufacturing industries, producing around 100 million m2 of plywood products annually. These industries are primarily located in the districts of Hoshiarpur, Ludhiana, Jalandhar, and Rupnagar.
Logs of poplar & eucalyptus tree are used as raw material for producing veneers (thin wood layers) for plywood manufacturing. Boilers and Thermic Fluid Heaters (Thermopac) are used as biomass combustors in plywood industries. Steam from boilers or hot synthetic oil from Thermopac is used for drying of veneers & other operations. The in-house wood bark, peeled wood chips & waste veneers are used as fuel in the combustor furnace. The components of the fuel mixture significantly differ in characteristics especially in moisture content (20-55%) and variable size. The improper fuel feeding & combustion practices and inadequate air pollution control system in these industries is resulting in nuisance of black smoke from their stacks thus contributing in the deterioration of ambient air quality of the area and leading to public complaints that become a serious concern of PPCB.
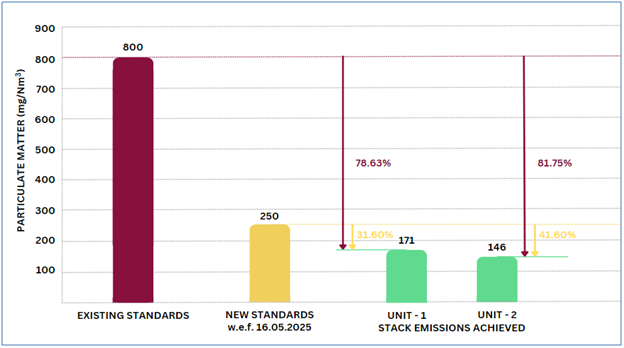
PSCST, under the project funded by Mission Tandrust Punjab, Directorate of Environment & Climate Change (DECC), Govt. of Punjab, has demonstrated pollution control technology in form of pulsejet bag filtration with specialized glass fiber bags and prepared standard operating procedure (SOPs) for operation and maintenance of the air pollution control system. The technology was successfully commissioned at M/s. Harisar Industrial Corporation, Ludhiana, in August 2023, and at M/s. KTM Plywood Pvt. Ltd., Hoshiarpur, in June 2024. The implementation of this technology has reduced particulate matter (PM) emissions by 75-80% in comparison to existing standards of 800 mg/Nm³ for agro waste based boilers with capacity ≥ 2TPH. Further these emissions are even 30-40% lesser than the new upcoming revised emission standards of 250 mg/Nm³ notified by MoEF&CC, GoI effective from May, 2025.
The salient achievements of the demonstrated technology include:
- Elimination of Black Smoke Emissions thus resulting in almost clearer skyline.
- Compliance to Revised PM Emission Standards with emission below 250 mg/Nm3.
- Dust capturing per unit - Approx. 500-700 kg per month.
The adoption of this technology by similar plywood units in the State will significantly reduce pollution and improve air quality of the region besides contribution to the envisaged targets of the Mission Tandrust Punjab.
Rolling Mills

Around 350 rerolling mills are operating in the State, which consume pulverized coal as fuel in their reheating furnace to heat the steel. During combustion of coal, emissions in the form of suspended particulate matter (SPM) are emitted at very high temperatures (400-650oC). The Council demonstrated two stage air pollution control technology (involving cyclone followed by scrubbing system) to contain high concentration of suspended ash particles within the prescribed limits of State Pollution Control Board. Around 300 rolling mills have adopted the pollution control technology evolved by the PSCST. The scientific design of APCD also resulted not only in controlling the air pollution but also reduced the fuel by 10% due to balanced draft of the furnace. The payback of the APCD is less than a year.
In addition, Council has been working on energy efficiency improvement in rerolling mills and has played a pivotal role by demonstrating Waste Heat Recovery System for dust laden gases, design of furnace, insulation of furnace and use of instrumentation. Council had demonstrated 135 energy efficient technologies in 62 rerolling mills with the support of UNDP. These interventions led to 5-15% energy savings in the sector.
These technologies have been demonstrated in the States of Chattishgarh, Gujarat as well as in Nepal.
Induction Units:
Around 200 induction furnaces with molten capacity of 3 T/heat - 30 T/heat are operating in the State. Earlier, these units had installed canopy hood to contain the dust emissions being generated during melting of scrap followed by Cyclonic scrubber/ Pulsejet bag filter with online cleaning as Air Pollution Control Device (APCD). Most of these furnaces have now started using magnet & pusher for charging of raw material into the furnace for faster melt rate which otherwise used to be manual. The benefits of using magnet & pusher are savings in heat time, enhanced productivity and lesser energy consumption. However, with the use of magnet & pusher, the operator has to keep the canopy hood away from the furnace resulting in poor suction efficiency at the hood leading to dispersion of emissions in the sheds and deterioration of ambient air quality.
To address this problem, PSCST after carrying out R&D studies, demonstrated Side Suction Hood (SSH) in one of the induction furnace units at Mandi Gobindgarh. The SPM concentration in stack was observed to less than 50 mg/Nm3 against the prescribed SPM standards of 150 mg/ Nm3. The SSH has been quite effective and appreciated by Punjab Pollution Control Board (PPCB) & Induction Furnace Association.
The technology has been adopted by around 178 induction units in the State. After adoption of technology, 100-250 kg (avg.) dust per day is being captured in the APCD of each unit. As such around 10,000 tonne dust per annum would be captured in 178 units which otherwise used to be dispersed into the atmosphere. The technology has significant contribution in improving the ambient air quality of Mandi Gobindgarh.

Cupola Units
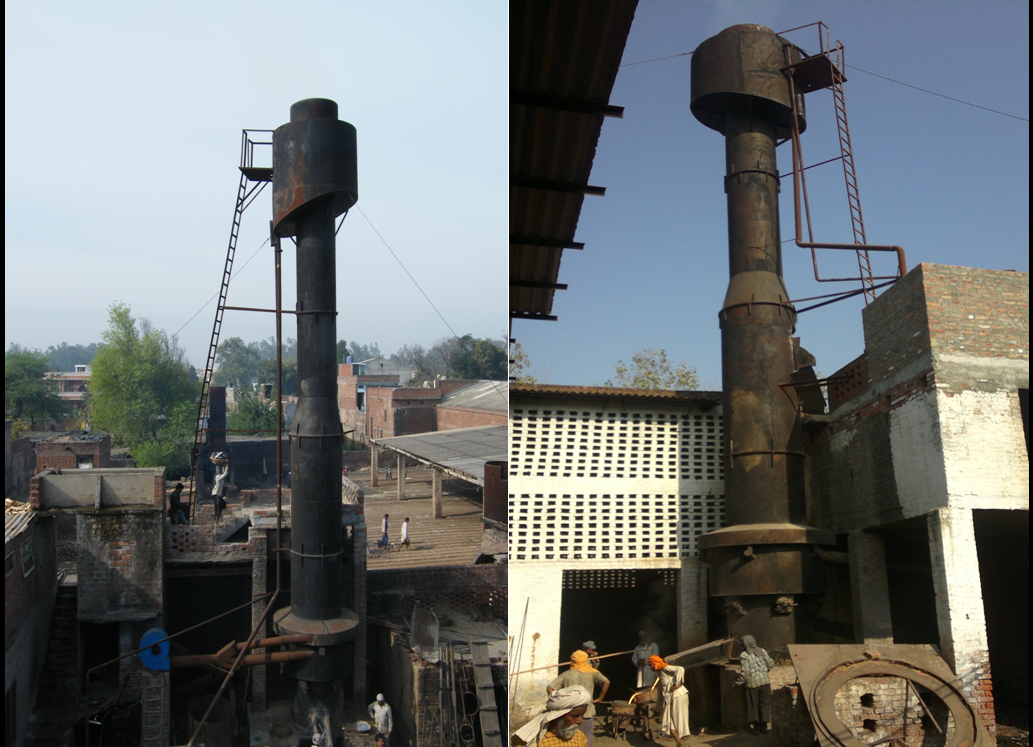

Cupola furnace is used for melting of pig iron for production of CI castings. Hard coke is used as fuel for melting the pig iron. During cupola operations, heavy emissions comprising metallic oxides, unburnt coke fine and CO are released in the surroundings. More than 900 cupola furnaces are operating in the State. PSCST demonstrated cost effective Air Pollution Control Technology comprising of a single stage scrubber in the form of wet cap mounted on the top of extended stack beyond cupola charging door. No power is required to run the APCD as thermal draft of flue gases is used to overcome the pressure drop. The water used for scrubbing is 100% recycled. The efficiency of APCD installed on the furnace is 70-80% and the pollution levels (SPM) after APCD were in the range of 210-275 mg/Nm3 against prescribed emission norms of 450 mg/Nm3. This technology has so far been replicated in more than 800 cupola units in the State.
Demonstration units have also been set up in the States of Haryana, Bihar, Jharkhand, Karnataka and J&K with support from Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), Department of Science and Technology (DST), GOI and Ministry of Environment & Forests. The Industry has reported economic savings to the tune of Rs. 2-8 lacs/annum with payback period of less than one year.
Hybrid & Induced Draft Brick Kilns
PSCST developed & demonstrated novel design of energy efficient hybrid brick kiln (kiln that can be operated on natural draft as well as induced draft depending on seasons i.e. winter or summer) with zigzag firing with support from DST, GoI. The technology has been approved by Punjab Pollution Control Board, so as to ensure mass replication of the cleaner technology in the State. The major benefits of the technology are reduced fuel consumption i.e 100-120 tonnes of coal/ kiln, reduction in GHG (300 tonnes CO2/ kiln) & SPM emissions reduction by 70-80% , drastic reduction in black smoke from chimney and improved brick quality by 15-20%.
Technology complies with new proposed national emission standards of 250 gm/Nm3. PSCST is also conducting district-wise capacity building programmes for the brick kiln owners & their workforce on better operating practices, as the technology is new and there is lack of trained manpower to effectively operate the technology. IEC booklets in local langurage have been developed on better construction practices.
The technology has been directly transferred in more than 850 brick kilns in Punjab and other States like Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu, Uttar Pradesh & Uttrakhand.
Rice Shellers
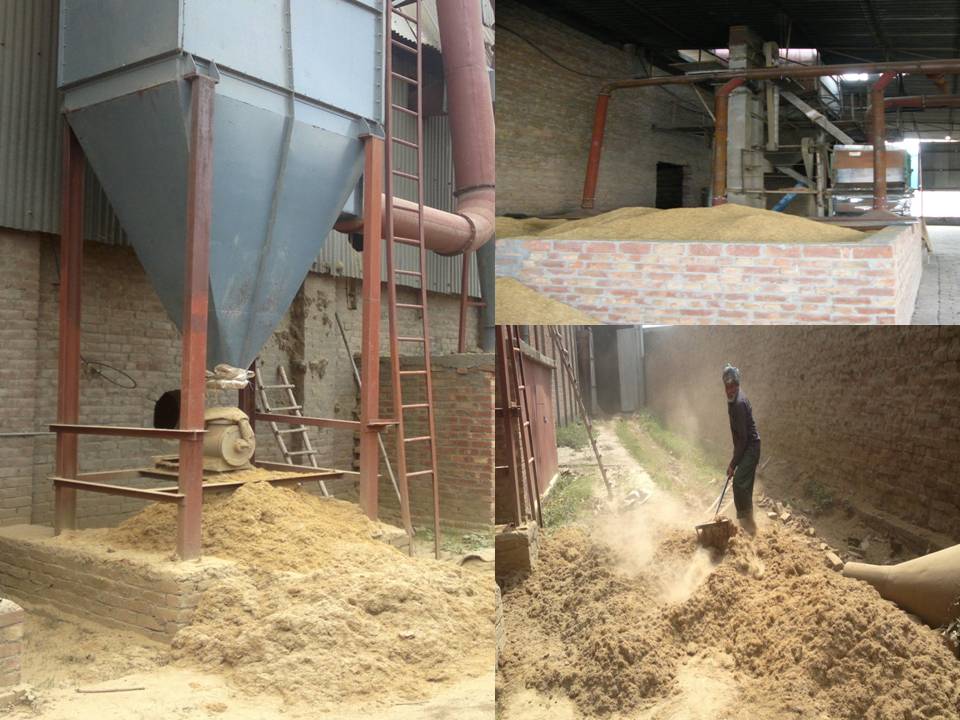

Rice shellers generate substantial amount of air pollution due to dust emitted from various sections of the shellers such as pre-cleaning, drying and milling due to inherent dust in the paddy received from fields/mandis. This leads to extremely difficult working conditions adversely affecting health of workers (especially respiratory problems), besides deteriorating ambient air quality.The Council had demonstrated technology for containment-cum-pollution control from various polluting sources of milling and drying section in dry rice shellers. The technology developed by the Council included set of cyclones in parallel followed by pulse jet bag filter.The cyclones effectively remove coarser particles which contribute to about 90% of the total dust load whereas Pulse Jet bag filters help in removal of fine particles. The Pulse Jet bag filtration technology has an advantage over the conventionally used shaker type bag filter as it requires 40-50% less area. The product quality has also been improved from capturing of dust in various stages in the plant.
Hot Dip Galvanizing Plants
A fume extraction system was designed with adequate hood suction velocity, duct network and specifications of ID fans and successfully demonstrated with multiple side suction hoods in a hot dip galvanizing plant for containment of fumes from zinc hot bath. The technology has potential for replication in similar units across the country.