Technologies to Address State's Key Challenges
Tech Support for Technology Demonstration
Steel Re-rolling Mills
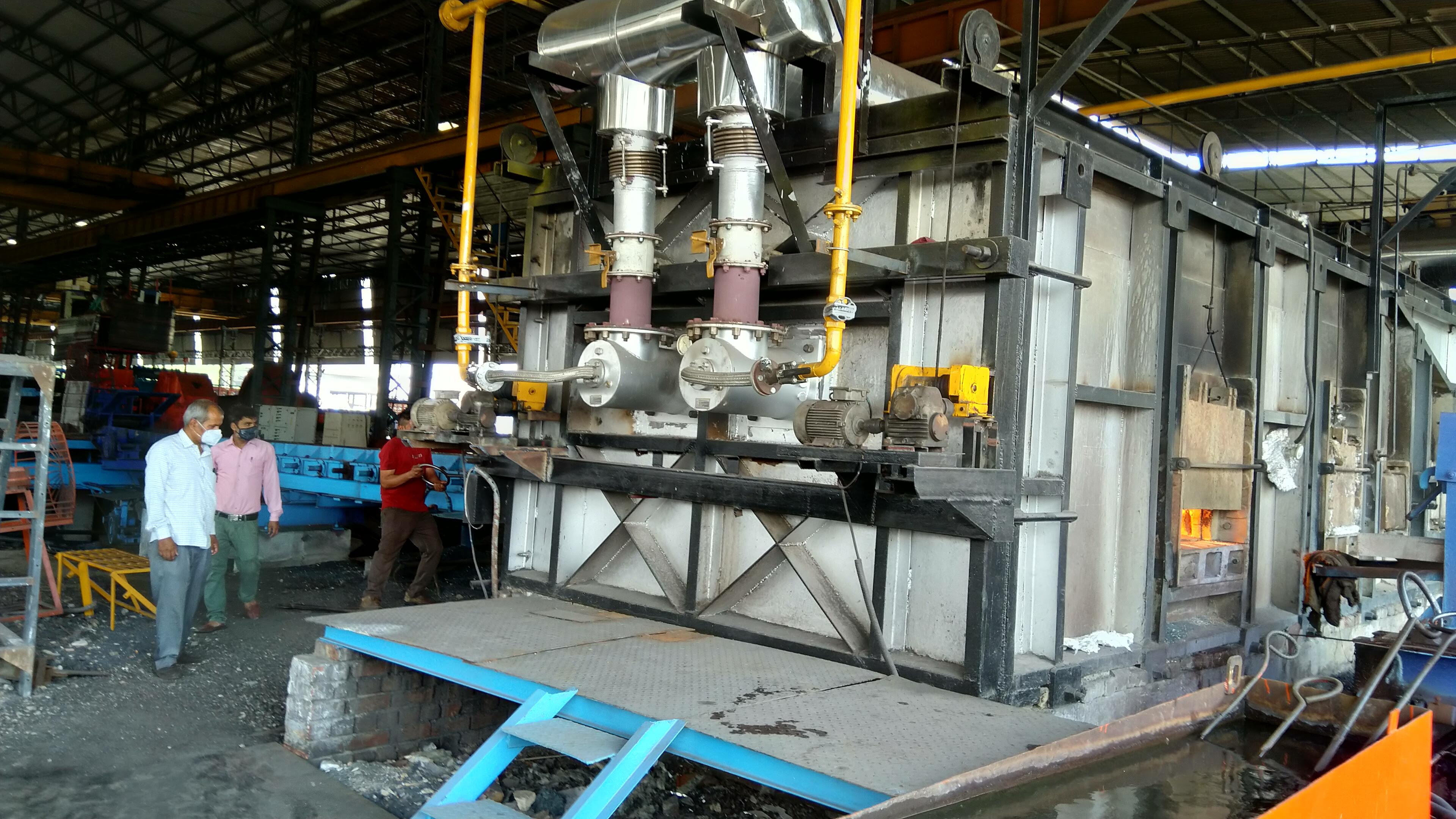

Mandi Gobindgarh and Khanna, the Steel Towns of Asia, have a cluster of industries comprising induction furnaces, rerolling mills and foundry units. The continuous operation of these industrial units has lead to generation of large amount of GHG & particulate emissions and these cities have been declared as Non-Attainment Cities of Punjab.
Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change, Government of India has launched National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in the year 2019 for tackling the problem of air pollution across the country in a comprehensive manner with a target to achieve 20-30% reduction in particulate emissions by 2024. The State has prepared an Action Plan, which include promotion of Piped Natural Gas in place coal and furnace oil in around 300 rerolling units operating in Mandi Gobindgarh and Khanna Cluster. This cluster consumes around 3 lakh tonne of coal as fuel to produce around 50 lakh tonnes of steel products annually. In this process, around 7.7 lakh tonnes of GHG emissions, 0.2 lakh tonnes of SO2 and 600 tonne of particulate matter is emitted in the atmosphere annually. Inspite of efforts by State Government and in the absence of model demonstration unit, the industry was not very confident and inclined towards adoption of PNG in place of coal.
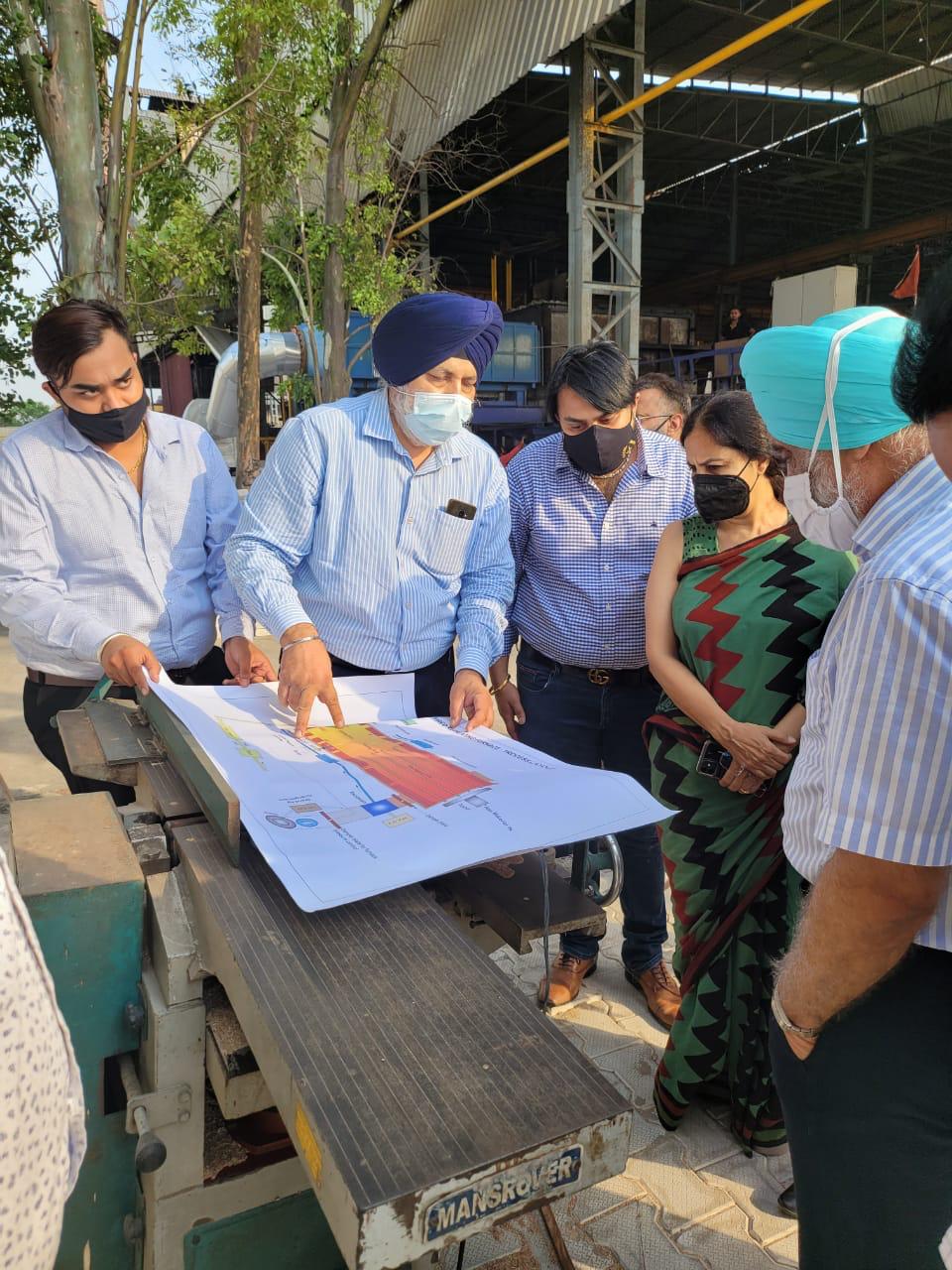

Punjab State Council for Science & Technology, despite COVID conditions, took up the challenge of establishing 3 model demonstration units representing varied categories of re-rolling mills in Mandi Gobindgarh & Khanna i.e. based on production capacity, raw material and output. The detailed studies of these units were conducted to establish baseline data w.r.t. production cost, scale loss and fuel consumption etc. PSCST thereafter developed the interventions for switch over to PNG by introducing mass based automation & control system based technology for the first time in the State. The other technical interventions include furnace modification, insulation type, high efficiency waste heat recovery system etc.
Based on this Novel tech intervention, 3 demonstration units have been set up in Mandi Gobindgarh viz at M/s. Royal Alloys (100 TPD), M/s. Bhartam Ispat Udyog (150 TPD) and M/s Rajshree Udyog (50 TPD). These units serve as model units for promoting wide scale replication of technology from coal to PNG for all steel re rolling mills of Mandi Gobindgarh & Khanna cluster. The development and demonstration of above technological innovations has resulted in reduction of Green House Gas emission to the tune of 40% and particulate matter emission reduction by more than 90%. Further, it has provided cleaner work zone environment to the industrial workforce which is around 100-125 workers per industrial unit.
The industry is also reaping economic benefits as the technological intervention developed and demonstrated by PSCST has established low PNG consumption (32-36 Sm³/Ton) and reduction in scale loss bringing in material saving of about 300 ton per year for a unit with average capacity of 10-15 ton per hour leading to monitory saving of more than Rs. 1.0 crore per annum to the industry.
Further, it also lead to the improved life cycle of plant and machinery thereby addressing the prevalent problem of corrosion of machinery parts due to high sulphur content in coal. It has also improved the product quality leading to better marketability.
The unique tech intervention developed by Council has paved way for taking steel rerolling mills cluster towards Industry 4.0 as many of the process operations have been automated, thereby, minimizing manual interventions. The adoption of these interventions by steel rerolling mill cluster would result in cleaner work zone environment for 25000 workforce and cleaner ambient air to the 2.5 lakh population of these cities. The model units set up by the Council have set up a benchmark for the steel re-rolling sector for emulation by other States too.
Agro-Residue Management
Punjab is predominantly an agricultural State and considered as the food bowl of India. Besides providing food grains the State also generates large amount of agro-waste. The proper management & utilization of this agro waste mainly paddy straw is one of the major challenges not only for the State but for the entire Nation. Punjab generates around 20 million tons of paddy straw annually out of which approx. 60-65% is burnt in open fields thus releasing green house gases (22-24 million tonnes of CO2 eqv./ annum), dust particles & other noxious gases in the environment.
The studies conducted by Council and many other R&D organizations have indicated that paddy straw has a calorific value ranging between 3200 - 3600 kcal/kg and has a potential to replace coal in industries such as boilers, brick kilns & power plants. But various O&M and transportation related problems are faced while using paddy straw due to it's low bulk density (transportation issues), high silica content (chopping/ processing issues) and presence of potassium & chlorides.
Council is working towards ex-situ management & utilization of paddy straw by replacing fossil fuels and developing it as green fuel. Council has successfully demonstrated the first-of-its-kind paddy straw based briquetting plant of 24 TPD (5000 TPA) capacity in Aspirational District Moga and another plant of same capacity is under installation in the District Patiala in the State of Punjab with financial support of MoEF&CC , GoI.
The various R&D studies conducted by Council includes:
- Manufacturing and utilization of paddy straw briquettes as replacement of fossil fuel in brick kilns.
- Improvement in design & metallurgy of paddy straw chopper blades.
- Development & field demonstration of paddy straw based briquetting for decentralized applications in the State of Punjab.
Tech Support for Environmental Monitoring
Development of Sensor Based System for Online Monitoring of River Water Quality of Punjab
The river sustain urbanization, industrialization, agriculture etc., however, there has been continuous degradation of the quality river waters due to contamination from anthropogenic activities. The effective monitoring of various parameters of river water is an important step for controlling the river pollution.
PSCST has signed an MoU with IIT, Ropar to develop a low cost online system using sensor based technology for the measurement/quantification of different parameters such as pH, TDS, Conductivity, BOD, DO and COD of river water quality of Punjab. The data received on cloud would be analyzed using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to generate automatic alerts if any parameter exceeds the prescribed limit.
Development of Integrated Dashboard for Real Time Data Monitoring in Punjab
The monitoring of quality of air, river waters and industrial and domestic effluents being treated at CETPs/ ETPs and STPs is one of the key challenge for ensuring clean air and clean water. Online monitoring stations for monitoring Ambient Air Quality, stack emissions, treated effluent quality are being installed in various industries in the State. The quantum of data generation is huge and the same is difficult to monitor and interpret manually.
Council is facilitating in the development of integrated portal which will receive the data in real time and analyze it to generate trends & reports using Artificial Intelligence and big data analytics which can be utilized in making enforcement, regulatory policies and effective interventions leading to a better environment.
Point-of-contact for industrial units/ industrial associations for seeking technical consultancy
Er. Pritpal Singh
Executive Director
Mobile: 9814104784
Email: pritpal.singh8[at]punjabmail[dot]gov[dot]in