Punjab State Climate Change Knowledge Centre (PSCCKC) has been established in Punjab State Council for Science and Technology (PSCST) with the support of Department of Science & Technology (DST), Government of India under National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change (NMSKCC) with an aim to cater the information and knowledge needs of policy makers, scientific community and general public to address regional climate change challenges.
Awards
-
SDG Action Award 2020
 SDG Action Award (2020) for ‘Environment Sustainability’ instituted by Department of Planning, Punjab and UNDP for promoting cleaner technologies to enhance State’s climate resilience capacity.
SDG Action Award (2020) for ‘Environment Sustainability’ instituted by Department of Planning, Punjab and UNDP for promoting cleaner technologies to enhance State’s climate resilience capacity. -
RCE Recognition Awards
 RCE Award (2022) for book on ‘Activity book on climate change’ from Institute for the Advanced Study of Sustainability, United Nations University, Japan.
RCE Award (2022) for book on ‘Activity book on climate change’ from Institute for the Advanced Study of Sustainability, United Nations University, Japan. -
Best State Award for promoting Green Schools
 Best State Award on Environment Audit in schools (2017) under Green Schools Programme from Centre for Science and environment, New Delhi
Best State Award on Environment Audit in schools (2017) under Green Schools Programme from Centre for Science and environment, New Delhi
Objectives
-

Assessment of climate change vulnerability of the State at block & sectoral levels
-

Develop database pertaining to climate parameters, environment & climate change issues of various sectors
-

Create Knowledge network by colloborating with national and international academics, research institutions & industries
-

Mainstreaming of climate change adaptation in developmental programmes of the State
-

Building institutional capacities by involving universities & research institutions
-

Interventions to enhance adaptive capacities of rural communities
-

Organize Capacity building programes, training, workshops on climate change aspects for various stakeholders
-

To provide support to climate change adaptation projects
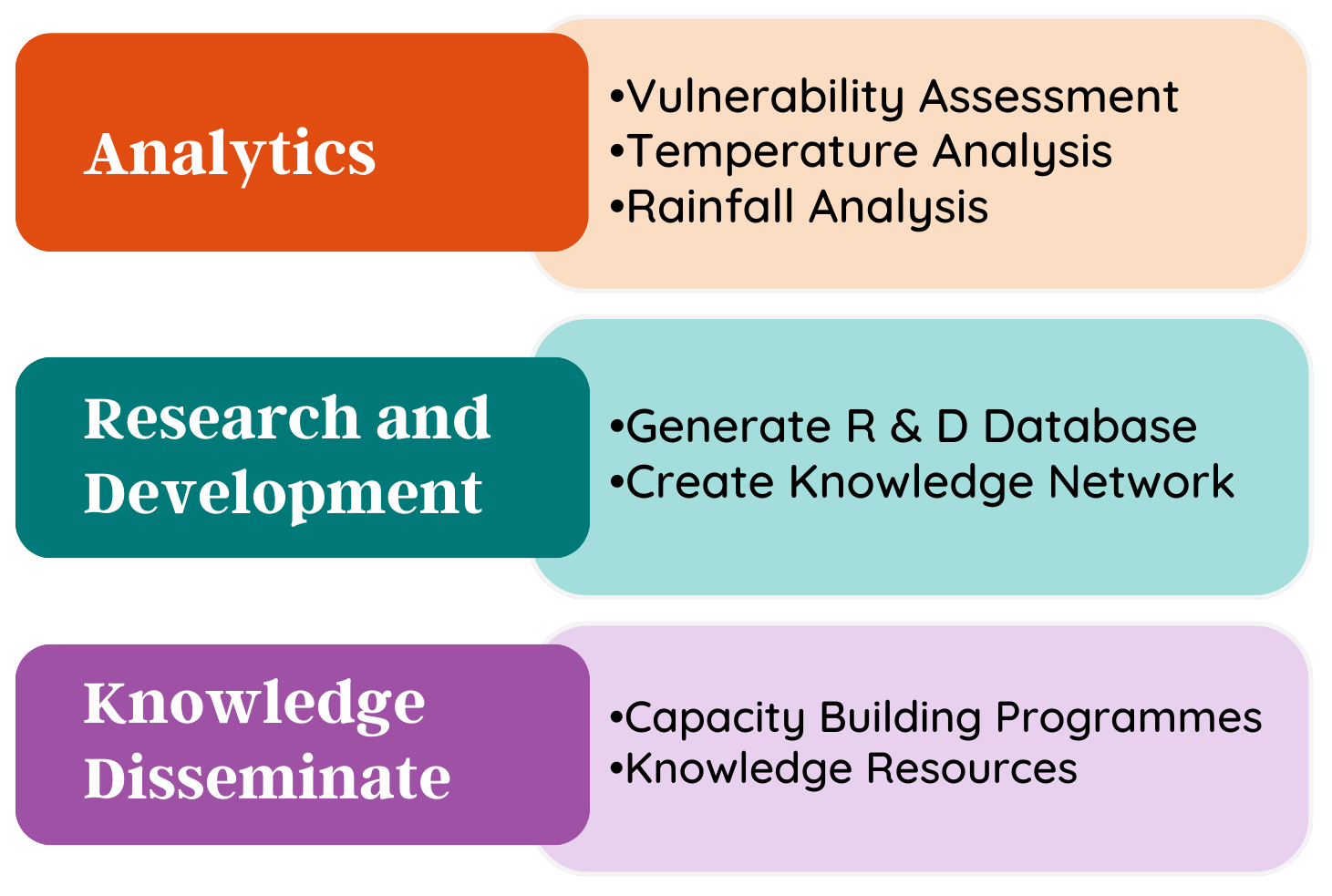
Activities initiated in line with the approved major objectives
Vulnerability Assessment
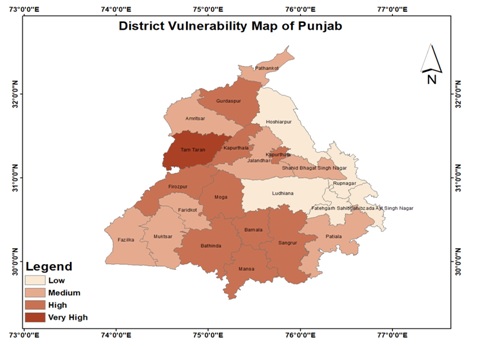
Vulnerability Assessment (VA) is the method of identification classification, quantification, and prioritization the regions and sectors which are likely to be adversely affected by climate change. Understanding climate change vulnerabilities is necessary for generating knowledge that can navigate states in a climate change scenario and hence plays a dominant role in developing as well as prioritizing the strategies for adaptation and mitigation. PSCCKC conducted a climate change vulnerability assessment in 22 districts of the state by using 15 indicators as per the uniform National Framework of DST.
The range of the Vulnerability was divided into four categories as under:
- Low : 0.45 to 0.55
- Medium : 0.55 to 0.60
- High : 0.60 to 0.70
- Very high : 0.70 to 0.80
Based on the categorisation, Tarn Taran has very high vulnerability towards climate change, followed by eight districts categorised as high vulnerability and further eight districts as medium vulnerability. The remaining five districts namely Hoshiarpur, Rupnagar, Fatehgarh Sahib, SAS Nagar and Ludhiana have low vulnerability Punjab State Climate Change Knowledge Centre has planned to carry out vulnerability assessment at block level as well for the key sectors of the State including agriculture and water sectors, in near future.
Climate parameters analysis
Climate parameters indicate the climate of a specific location or region such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed and humidity etc. Temperatures differ significantly around the globe depending on natural and anthropogenic activities. IPCC reports have already shown through several evidences that the climate is changing across our planet. Analysis of climate parameters i.e Temperature and rainfall are significant to better know about the climate change in present and future scenarios.
Temperature
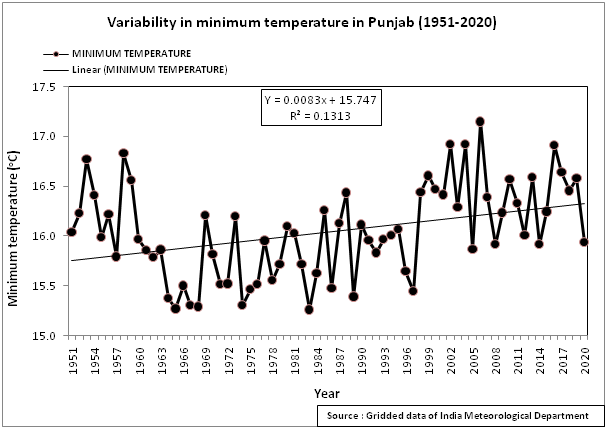
The analysis of India Meteorological Department (IMD) data from 1950 to 2020 has indicated no significant increase in maximum temperature, however, significant increase in minimum temperature has been observed across the State.
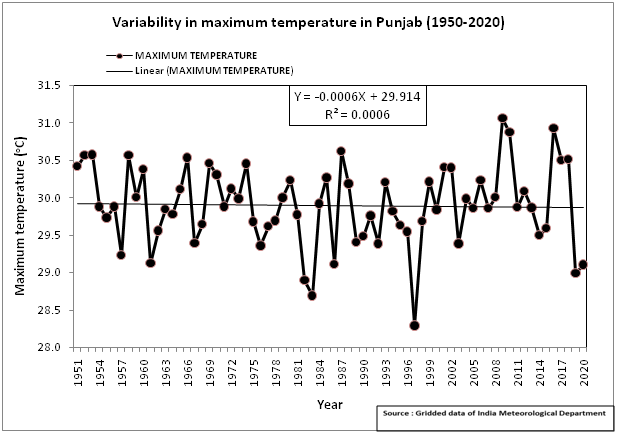
- The average maximum temperature ranged from 28.3°C to 31.1°C during 1950-2020
- The average minimum temperature ranged from 15.3°C to 17.1°C during 1950-2020
As per study based on CORDEX South Asia model, average annual maximum temperature for RCP4.5 scenario is projected to increase by about 1.2°C towards Mid-Century (MC) and by 2.1°C towards End-Century (EC). However, for RCP 8.5 scenario, it is projected to increase by about 1.4°C towards MC and 4.5°C towards EC.
Average annual minimum temperature for RCP4.5 scenario is projected to increase by about 1.3°C towards MC and by 2.5°C towards EC. Whereas, it is projected to increase by about 1.7°C towards MC and 5.2°C towards EC for RCP8.5 scenario.
Rainfall
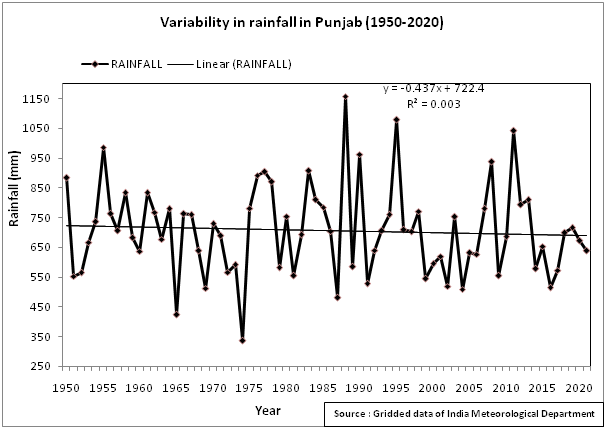
The IMD gridded data analysis has indicated a large variation in decadal rainfall over the State. The annual rainfall during the period 1951-2021 ranged from 335.7 mm to 1157.8 mm. The rainfall pattern was observed to be erratic over the years in the state.
The highest rainfall increasing trend in post monsoon season while decreasing trend in winter and pre-monsoon season has been projected towards MC and EC for both RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 scenarios. Average annual rainfall for RCP 4.5 scenario is projected to increase by 5.4% towards MC and 12.5% towards EC. While for RCP 8.5 scenario, increase by 9.8% towards MC and 12.8% towards EC.
Database of Published Literature
Developing database of research by periodic updation of literature published pertaining to environment & climate change of various sectors will support researchers with baseline information w.r.t studies already conducted. Further, the database will generate new knowledge among policy makers to support planning of appropriate local adaptation programs for the sector vulnerable to climate change.
Knowledge Network
The Centre signed Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) with 14 State universities/research institutions for partnering to undertake state specific collaborative programs to tackle environmental and climate change related challenges. A network of 100 colleges for percolation of knowledge on climate change issues established in collaboration with Centre for Restoration of Ecosystem of Punjab (CRESP) of Punjabi University, Patiala. The Centre is also working in collaboration with 5500 ecoclubs of state through National Green Corps (NGC) a nationwide initiative of MoEFCC.
Further, Centre has initiated International collaboration with the following:-
- The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), Nepal for tech interventions on energy efficient cleaner and low carbon technologies.
- Institute for Governance & Sustainable Development (IGSD) for building strategy to effectively control non-CO2 emissions and other Short-lived Climate Pollutants (SLCPs), particularly in Agriculture, Livestock & Health sectors.
- Institute of Nuclear Energy Research (INER), Taiwan for exploring technologies for conversion of waste to renewable energy
- Canadian High Commission, Canada for Climate Action and enhancing resilience of rural women and the underprivileged.
Regional Partners

International Partners

Punjab- State Action Plan on Climate Change (SAPCC)
National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) has been launched in the year 2008 to address climate-related issues. To align National strategies adopted in NAPCC with the regional priorities & developmental needs Punjab has formulated first guiding document Punjab State’s Action Plan on Climate Change (SAPCC 1.0) for the year 2014-2020 to accelerate adaptation and mitigation actions at the regional level. The State has taken a large number of initiatives as per strategies outlined in the SAPCC 1.0.
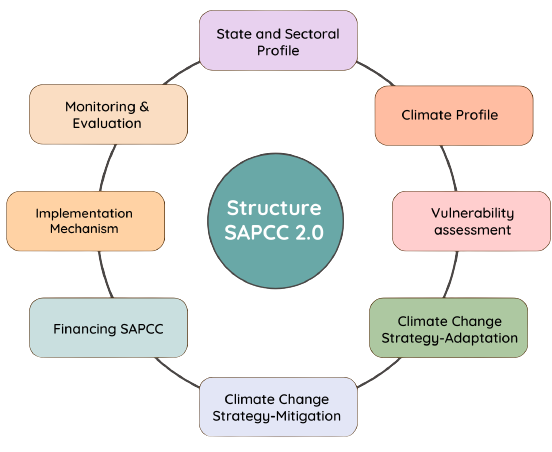
The final draft of SAPCC 2.0 has been prepared for the period till 2030 through extensive consultations with relevant stakeholder departments of the state for integrating climate change concerns in existing schemes/programmes. One-to-one meetings with >25 State line departments & >15 Research Institutes held for finalizing sectoral strategies.
SAPCC 2.0 comprises of following 7 missions :-



Capacity Building Programmes
Holistic approach is basic requirement for appropriately addressing climate change concerns. For integrated knowledge dissemination on climate change aspects, centre will organize Capacity Building programmes such as workshop, seminar, conference and training for Govt officials, Academic institutions, farmers, rural women, Community-Based Organizations (CBOs) & Non Government Organization (NGOs)

.jpg)
.jpg)